Building a Fluorite Processing Plant: A Comprehensive Guide
 Essow
Essow
 Feb 28, 2024
Feb 28, 2024
 1114
1114
If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!
Constructing a fluorite processing plant is a multifaceted endeavor that encompasses mineral processing, civil engineering, mine design, and resource exploration. This comprehensive guide provides you with the essential steps and considerations for building a successful fluorite processing facility.
Fluorite, a mineral composed mainly of calcium fluoride (CaF2), is a valuable commodity due to its diverse applications in the steel, aluminum, chemical, and glass industries. It is also used in the production of hydrofluoric acid, which is a key component in various industrial processes. With the growing demand for fluorite, establishing a processing plant can be a lucrative venture. However, it requires careful planning and execution to ensure efficiency, safety, and environmental compliance.
A feasibility study and market analysis are critical components of the preliminary stages of establishing a fluorite processing plant. These assessments help determine the viability of the project, its potential profitability, and the risks involved. Here's a deeper look into these two essential steps:
01 Feasibility Study
BackA feasibility study is an evaluation of the practicality of a project. It involves a detailed examination of the technical, financial, legal, operational, and scheduling aspects of the proposed plant. The main objectives of a feasibility study for a fluorite processing plant are:
Technical Feasibility: Assessing whether the proposed plant can be built and operated to meet the desired production levels. This includes evaluating the available technology, the suitability of the chosen location, and the availability of skilled labor.
Economic Feasibility: Estimating the costs involved in establishing and operating the plant, including capital expenditure (CAPEX), operational expenditure (OPEX), and the potential return on investment (ROI). It involves creating financial models to analyze the project's profitability under various scenarios.
Legal and Regulatory Feasibility: Ensuring that the project complies with all relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. This includes environmental impact assessments, obtaining necessary permits, and understanding the legal obligations of the project.
Operational Feasibility: Evaluating the operational aspects of the plant, such as the management structure, supply chain logistics, and the day-to-day running of the facility.
Scheduling Feasibility: Developing a realistic timeline for the project, from construction to operational start-up, and identifying any potential bottlenecks or delays.
02 Market Analysis
BackMarket analysis is a pivotal step in the development of any industrial project, including the establishment of a fluorite processing plant. It provides insights into the dynamics of the fluorite market, which is essential for strategic planning and decision-making. Here's an in-depth look at the various aspects of market analysis:
1. Industry Trends and Growth Potential
Understanding the historical trends and current state of the fluorite industry is crucial. This includes analyzing the factors that have influenced the industry's growth, such as technological advancements, changes in end-use applications, and global economic conditions. Forecasting the future growth potential involves examining the demand drivers, such as the expansion of the steel and aluminum industries, which are significant consumers of fluorite.
2. End-Use Applications
Fluorite has a wide range of applications, including the production of hydrofluoric acid, which is used in various industries like glass manufacturing, semiconductor production, and the refining of metals. A detailed analysis of these applications helps identify the market segments with the highest growth potential and the specific quality requirements for fluorite in each segment.
3. Supply Chain Analysis
A comprehensive review of the fluorite supply chain is necessary to understand the availability of raw materials, the capacity of existing mines, and the operational status of processing plants. This analysis also includes the identification of potential suppliers, their production capacities, and the reliability of their supply.
4. Competitive Landscape
Identifying the key competitors in the fluorite market is essential for understanding the market share, pricing strategies, and competitive advantages. This includes both existing players and potential new entrants. An analysis of their production costs, quality of products, and market positioning can provide valuable insights into the competitive environment.
5. Price Fluctuations and Determinants
The price of fluorite can be influenced by various factors, such as supply and demand dynamics, transportation costs, and geopolitical events. A historical price analysis can help identify patterns and trends, while a forward-looking analysis can predict future price movements based on expected changes in the market.
6. Market Segmentation
Segmenting the market based on product type (acid-grade, metallurgical-grade, etc.), end-use industry, and geographical region allows for a more targeted approach to marketing and sales. Each segment may have different growth rates, price sensitivities, and quality requirements, which are crucial for tailoring the business strategy.
7. Regulatory Environment
The regulatory environment can significantly impact the fluorite market. Environmental regulations, mining laws, and trade policies can affect the cost of production, the availability of raw materials, and the competitiveness of the product in the market. Staying informed about regulatory changes is essential for compliance and strategic planning.
8. Risk Assessment
Market risks can stem from various sources, such as economic downturns, changes in consumer preferences, or the emergence of alternative materials. A thorough risk assessment helps in developing contingency plans and strategies to mitigate potential adverse effects on the business.
9. Customer Analysis
Understanding the needs and preferences of customers is vital for product development and marketing. This includes analyzing customer demographics, purchasing patterns, and feedback. Building strong relationships with customers can lead to long-term partnerships and a better understanding of market needs.
10. Distribution Channels
Identifying the most effective distribution channels for fluorite products is crucial for reaching the target market. This may involve partnerships with distributors, direct sales to end-users, or online platforms. The choice of distribution channels can impact the cost structure and the speed of reaching customers.2. Site Selection and Permitting
Choosing the right location for your plant is a critical decision. Factors to consider include proximity to the fluorite deposit, accessibility to transportation networks, availability of water and power, and compliance with environmental regulations. Securing the necessary permits and licenses from local and federal authorities is also a prerequisite for any mining and processing operation.
03 Plant Design and Engineering
BackThe design and engineering phase of a fluorite processing plant is a meticulous process that lays the foundation for the plant's operational efficiency, safety, and environmental compliance. This phase involves several critical steps and considerations:
1. Process Flowsheet Design
The process flowsheet is a detailed representation of the sequence of operations involved in processing fluorite ore. It starts with the extraction and crushing of the ore, followed by grinding, classification, flotation, and finally, concentration and dewatering. The design must ensure that each stage is optimized for the specific characteristics of the fluorite deposit, such as its size, hardness, and purity.
2. Equipment Selection
Choosing the right equipment is crucial for the plant's performance. This includes primary crushers, ball mills, flotation cells, thickeners, and filters. The selection should be based on factors such as the plant's capacity, the nature of the ore, energy efficiency, and the availability of spare parts and maintenance services.
3. Plant Layout
The layout of the plant should facilitate smooth material flow, minimize transportation distances, and ensure that there is adequate space for maintenance and expansion. It should also consider safety zones, emergency access routes, and the integration of auxiliary facilities such as workshops, storage areas, and laboratories.
4. Civil and Structural Engineering
The plant's infrastructure must be designed to withstand the loads imposed by the processing equipment and the weight of the materials. This includes the design of foundations, structural steelwork, and concrete structures. Geotechnical assessments are also necessary to ensure the stability of the site.
5. Utilities and Infrastructure
The plant requires a reliable supply of utilities such as water, electricity, and fuel. The design should include efficient systems for water management, including recycling and treatment, as well as power generation or distribution systems. Additionally, the plant's infrastructure should support the transportation of raw materials and finished products.
6. Environmental Considerations
Environmental protection is a critical aspect of plant design. This includes the management of waste products, such as tailings and slag, which must be stored or treated in an environmentally safe manner. The design should also incorporate measures to reduce emissions, noise, and dust, and to prevent water pollution.
7. Safety Systems
Safety is paramount in the design of a fluorite processing plant. This includes the incorporation of fire protection systems, emergency response plans, and safety features in the equipment design. The plant should also have adequate lighting, ventilation, and ergonomically designed workstations to protect the health and well-being of the workforce.
8. Automation and Control Systems
The integration of automation and control systems can significantly enhance the efficiency and reliability of the plant. This includes the use of process control software, sensors, and actuators to monitor and control the operations in real-time. Advanced systems can also facilitate predictive maintenance and optimize energy consumption.
9. Compliance with Standards and Regulations
The plant design must comply with all relevant industry standards, such as ISO, and local, national, and international regulations. This includes occupational health and safety standards, environmental protection regulations, and quality management systems.
10. Cost Estimation and Budgeting
Throughout the design and engineering phase, it is essential to estimate the costs accurately. This includes the capital costs for equipment, construction, and infrastructure, as well as the operational costs for utilities, labor, and maintenance. A detailed budget helps in securing financing and managing the project's finances effectively.
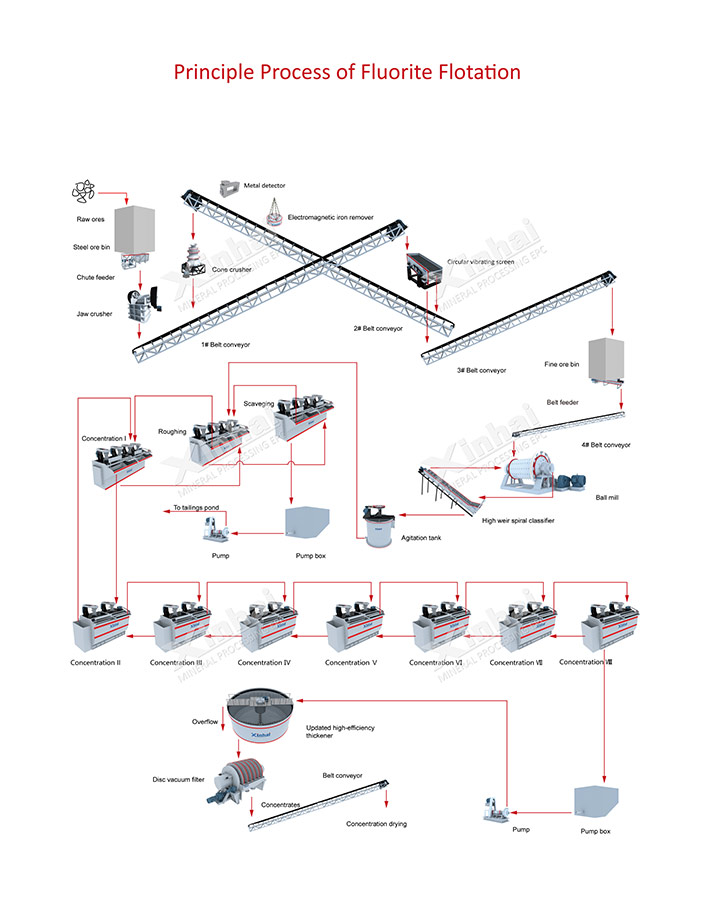
(Fluorite Processing Flowchart)
04 Equipment Procurement and Installation
BackThe procurement and installation of equipment are critical phases in the development of a fluorite processing plant. These steps ensure that the plant is equipped with the necessary machinery to operate efficiently and effectively. Here's a detailed look at the process:
1. Equipment Specification
The first step is to define the specifications for each piece of equipment based on the process flowsheet and plant design. This includes the capacity, size, material of construction, and any specific features required for the processing of fluorite. For example, ball mills need to be specified according to the size of the feed material and the desired product size.
2. Vendor Selection
Once the specifications are established, the next step is to identify and evaluate potential vendors. This involves researching the market, requesting for proposals, and comparing the offerings in terms of quality, price, after-sales support, and delivery timelines. It's essential to choose vendors with a proven track record in the mining industry and a reputation for reliability and performance.
Xinhai is a good choice, we can provide a whole line for fluorite processing, including designing, equipment manufacturing and operating.
3. Procurement Contracts
After selecting the vendors, procurement contracts are negotiated and finalized. These contracts should detail the scope of supply, delivery schedules, warranties, and performance guarantees. It's crucial to include clear terms and conditions to protect the interests of the plant owner and to ensure that the equipment meets the agreed-upon specifications.
4. Logistics and Transportation
The logistics of transporting the equipment to the plant site can be complex, especially for large and heavy machinery. This requires careful planning, including the selection of suitable transportation methods, obtaining necessary permits, and coordinating with the plant's construction schedule to ensure a smooth delivery.
5. Equipment Unloading and Storage
Upon arrival at the site, the equipment must be carefully unloaded and stored to prevent damage. This may involve the use of cranes, forklifts, or other heavy lifting equipment. The storage area should be secure and protected from the elements until the equipment is ready to be installed.
6. Installation and Commissioning
The installation of equipment is a precise operation that must be carried out according to the manufacturer's guidelines and the plant's engineering plans. This typically involves assembling large structures, aligning machinery, and connecting utilities such as power, water, and process lines. The installation team should consist of skilled technicians and engineers who are familiar with the specific equipment and safety procedures.
7. Pre-Commissioning Checks
Before the equipment is commissioned, it's essential to perform pre-commissioning checks. This includes verifying the alignment of machinery, checking for leaks, and ensuring that all safety devices are in place and functioning correctly. These checks help to identify and resolve any issues before the plant starts operating.
8. Commissioning and Testing
Commissioning involves starting up the equipment and running it under controlled conditions to ensure that it operates as intended. This may include running tests to verify the performance of the equipment, such as the efficiency of the ball mills or the separation capabilities of the flotation cells. Any issues identified during testing should be addressed before moving to the next stage.
9. Operator Training
To ensure safe and efficient operation, it's crucial to train the plant operators on the use and maintenance of the equipment. This training should be provided by the equipment manufacturers or qualified trainers and cover all aspects of operation, including emergency procedures and troubleshooting.
10. Final Handover
Once the equipment has been successfully commissioned and tested, and the operators have been trained, the final handover takes place. This marks the completion of the procurement and installation phase, and the plant is ready to commence production.

(Fluorite flotation plant)
05 Other Considerations
Back1. Environmental and Safety Considerations
Environmental protection and worker safety are paramount in the mining industry. The plant design should incorporate measures to minimize waste, prevent pollution, and manage hazardous materials. This includes the treatment of tailings, the containment of dust and emissions, and the implementation of safety protocols for all operations.
2. Commissioning and Operational Readiness
Before the plant can commence operations, it must undergo a rigorous commissioning process. This involves testing all equipment and systems to ensure they function as intended. Staff training is also a critical component of operational readiness, ensuring that all personnel are familiar with the plant's processes and safety procedures.
3. Ongoing Maintenance and Optimization
Once the plant is operational, regular maintenance is essential to sustain its performance and prevent downtime. This includes routine inspections, equipment repairs, and the replacement of worn parts. Additionally, ongoing optimization efforts can enhance the plant's efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the quality of the processed fluorite.

(Automatic monitoring system)
4. Compliance and Reporting
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is mandatory for any fluorite processing plant. This includes regular reporting of production data, environmental impact assessments, and adherence to health and safety regulations. Establishing a robust compliance program can help avoid fines, penalties, and reputational damage.
06To Wrap Up
BackBuilding a fluorite processing plant is a complex but rewarding endeavor. By following this comprehensive guide, you can navigate the challenges of site selection, plant design, equipment procurement, environmental considerations, and operational management. With careful planning and execution, your fluorite processing plant can become a sustainable and profitable operation, contributing to the growth of the fluorite industry and the broader economy.
If you need to build a fluorite processing plant, feel free to contact our online customer service or leave a message, our technician would contact you as soon as possible to help you finish this whole process.
 +86 18716000713
+86 18716000713 xlyin@xinhaimining.net
xlyin@xinhaimining.net




 Message
Message Chat Now
Chat Now



















