How to Choose Antimony Processing Technology?
 Sheena
Sheena
 Apr 21, 2025
Apr 21, 2025
 21
21
If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!

antimony extraction plant
Choosing the right antimony processing technology depends on several key factors related to the type of ore, desired end-product, economic feasibility, and environmental considerations. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help evaluate and choose the most suitable processing technology:
01Identify the Type of Antimony Ore
BackThere are three main types of antimony ores, and each requires a different processing approach:
| Ore Type | Description | Common Processing Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Stibnite (Sb₂S₃) | Sulfide ore (most common) | Flotation, roasting followed by reduction |
| Oxide ores | Formed by weathering of sulfides | Gravity separation, leaching |
| Mixed ores | Contain both sulfide and oxide | Combined or selective processing |
02Define Your Processing Goals
BackDecide on:
End-product: Antimony trioxide (Sb₂O₃), antimony metal, or antimony sulfide.
Purity requirements: High-purity may require more complex refining steps.
Scale of operation: Small-scale vs industrial-scale.
Byproduct recovery: Consider gold, silver, or arsenic if present.
03Evaluate Common Processing Technologies
BackA. Flotation
Best for: Sulfide ores like stibnite.
Pros: High recovery, mature technology.
Cons: Requires good ore liberation, uses chemicals.
B. Gravity Separation
Best for: Coarse oxide ores or ores with high SG contrast.
Pros: Low cost, eco-friendly.
Cons: Lower recovery for fine particles.
C. Hydrometallurgy (Leaching)
Best for: Oxidized or low-grade ores.
Reagents: NaOH, Na₂S, or acidic leaching.
Pros: Lower emissions, good for fine-grained ores.
Cons: Slower, reagent cost, waste management.
D. Pyrometallurgy (Roasting + Reduction)
Steps:
Roast sulfide to antimony oxide.
Reduce oxide with carbon to metallic antimony.
Pros: Produces high-purity metal.
Cons: Energy-intensive, produces SO₂ gas (needs scrubbing).
04Consider Economic and Environmental Factors
BackCapEx & OpEx: Cost of equipment, energy, reagents, and labor.
Waste management: Tailings, emissions (SO₂), arsenic handling.
Water and energy availability
Regulations and permitting in your country
05Pilot Testing & Process Design
BackBefore scaling up:
Conduct bench-scale and pilot tests.
Perform mineralogical analysis.
Test different flowsheets for recovery rate, selectivity, and economics.
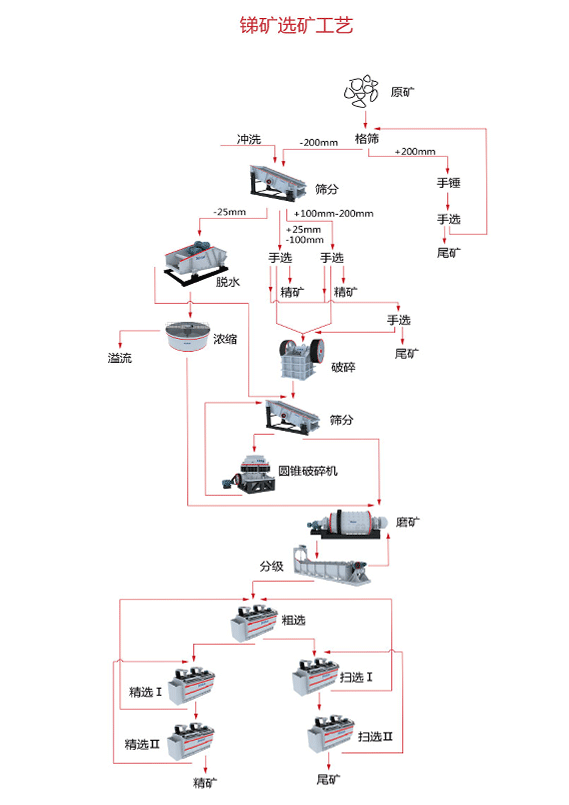
06Recommended Process Flow Examples
BackExample 1: Stibnite Ore
Crushing → Grinding → Flotation → Roasting → Reduction → Refining
Example 2: Oxide Ore
Crushing → Gravity Separation or Alkaline Leaching → Precipitation → Refining
07Final Tip:
BackCustom design is key. Partner with experienced metallurgical consultants or EPC firms who can tailor a solution based on ore characteristics and business goals. Would you like help comparing specific technologies or designing a sample processing flow for a certain type of ore? Contact us for more details.
 +86 18716000713
+86 18716000713 xlyin@xinhaimining.net
xlyin@xinhaimining.net




 Message
Message Chat Now
Chat Now

















