What's the Cost of Copper Processing Plant?
 Sheena
Sheena
 Nov 23, 2024
Nov 23, 2024
 1230
1230
If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!

Site-map-of-Pakistan-copper-ore-plant
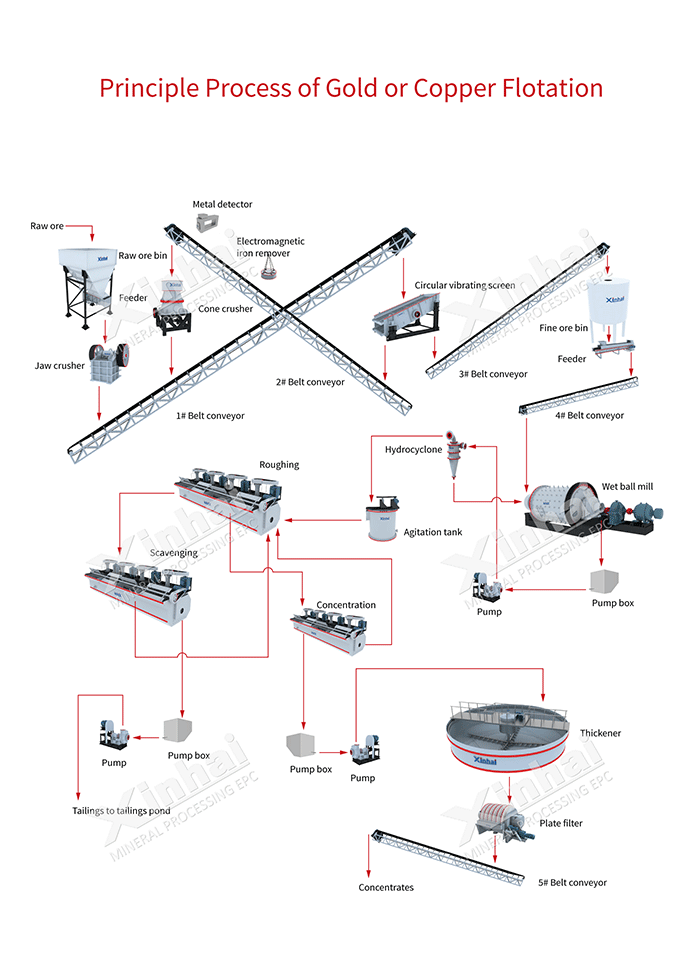
The cost of a copper processing plant varies significantly depending on several factors, including its capacity, location, the level of technology employed, and whether it includes additional refining stages like smelting or electrolysis. Before we explained how to extract copper from raw ore. Here's a breakdown of the main factors influencing the cost:
01Capital Expenditure (CapEx)
Back1. Small to Medium Scale Plants
Capacity: Typically processes tens of thousands of tons of ore annually.
Description: These are plants with simpler processes, often involving basic crushing, grinding, and flotation to produce copper concentrate.
2. Large Scale Plants
Capacity: Millions of tons of ore annually.
Description: These plants often include advanced processing stages such as leaching, solvent extraction-electrowinning (SX/EW), or smelting and refining, making them capable of producing high-purity copper cathodes.
02Factors Affecting the Cost
Back1. Scale and Capacity
Larger plants with higher throughput require significant investment in infrastructure, equipment, and personnel.
2. Technology
Copper processing involves various stages, including crushing, grinding, flotation, smelting, and refining. Modern equipment enhances efficiency but comes at a higher cost. Advanced technology like SX/EW or bio-leaching increases efficiency but also raises costs. Modern automation systems and control technologies can boost performance and reduce operational costs but demand higher initial investment.
3. Location
Proximity to raw materials (ore deposits), utilities (electricity and water), and infrastructure (transportation and logistics) impacts construction costs. Remote locations often require additional investments in roads, power supplies, and worker accommodations.
4. Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
Stringent environmental laws can add to costs due to the need for advanced waste treatment systems, tailings management, and emissions control.
5. Construction and Material Costs
Local labor and material costs, which vary globally, significantly influence the budget. Skilled labor and technical expertise are essential for constructing and operating the plant. Local labor often more affordable but may require additional training. Specialized professionals required for design, engineering, and technology integration, increasing costs.
03Operating Expenditure (OpEx)
BackKey Elements:
1. Electricity: Copper processing is energy-intensive, particularly smelting and electrolysis stages. Pre-existing utilities like power, water, and roads can lower initial investment.
2. Labor: Skilled labor, particularly for technical and operational roles, influences ongoing costs.
3. Chemicals: Flotation reagents, sulfuric acid (for leaching), and other processing inputs. Adherence to environmental regulations is a major cost driver, especially in regions with stringent policies.
4. Maintenance: Equipment wear-and-tear, especially for crushers, mills, and conveyors.
04Summary
BackSmall-scale copper processing plants (basic operations, lower throughput) can cost as low as $1 million.
Mid-sized operations with moderate capacity and technology may cost $10-50 million.
Large-scale, high-capacity plants with state-of-the-art facilities can exceed $500 million to $1 billion.
Careful feasibility studies, accurate cost assessments, and strategic planning are crucial to ensure project viability and profitability.
 +86 18716000713
+86 18716000713 xlyin@xinhaimining.net
xlyin@xinhaimining.net




 Message
Message Chat Now
Chat Now

















