What Are the Mining Methods for Fluorite? A Simple Guide
 Laura
Laura
 Apr 01, 2025
Apr 01, 2025
 144
144
If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!

Vietnamese fluorite ore
Fluorite, also known as fluorspar, is a colorful mineral vital for steelmaking, chemicals, and even jewelry. But before it reaches factories, it must be extracted from the earth. This guide breaks down the main mining methods for fluorite, explaining how each works and where they're used—in plain language anyone can understand.
01 What Is Fluorite?
BackFluorite (calcium fluoride, CaF₂) is a soft, glow-in-the-dark mineral found in hues like purple, green, and blue. It's primarily mined for:
Metallurgy: Helps purify steel and aluminum.
Chemicals: Used to make hydrofluoric acid (for Teflon and refrigerants).
Gemstones: High-quality fluorite is cut into decorative stones.
02 3 Main Fluorite Mining Methods
Back1. Open-Pit Mining
1). How It Works:
Step 1: Remove soil and rock (overburden) covering the fluorite deposit.
Step 2: Use explosives and heavy machinery (excavators, trucks) to extract ore.
Step 3: Transport ore to processing plants for crushing and purification.
2). Where It's Used:
Shallow deposits (less than 100 meters deep).
Major Locations: China (world's largest producer), Mexico, Mongolia.
3). Pros:
Lower cost.
High production rates.
4). Cons:
Large environmental footprint (land disruption, dust).
Weather-dependent (rain can halt operations).
2. Underground Mining
1). How It Works:
Step 1: Dig vertical shafts or horizontal tunnels to reach deep fluorite veins.
Step 2: Use drills, explosives, or continuous miners to extract ore.
Step 3: Transport ore to the surface via conveyors or trucks.
2). Common Techniques:
Room-and-Pillar: Leaves "pillars" of ore to support the roof.
Cut-and-Fill: Removes ore in sections and backfills with waste rock.
3). Where It's Used:
Deep deposits (100+ meters underground).
Major Locations: Illinois (USA), South Africa, Spain.
4). Pros:
Less surface disruption.
Access to high-grade ores.
5). Cons:
Higher costs (ventilation, safety equipment).
Slower production.
3. Solution Mining (Less Common)
1). How It Works:
Step 1: Drill wells into the fluorite deposit.
Step 2: Pump water or acid to dissolve fluorite.
Step 3: Bring the fluorite-rich solution to the surface for processing.
2). Where It's Used:
Soluble fluorite deposits in porous rock.
Example: Experimental projects in China.
3). Pros:
Minimal land disturbance.
Works for deep or hard-to-reach ores.
4). Cons:
Limited to specific geology.
Risk of groundwater contamination.
03 Comparison of Fluorite Mining Methods
Back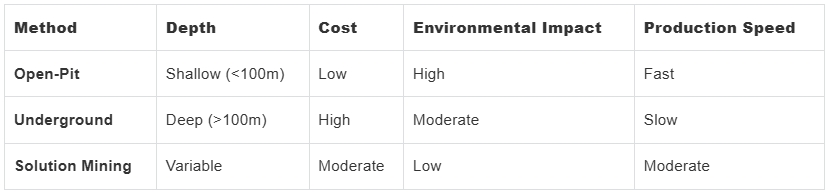
Fluorite Mining Methods
04 Factors Influencing Mining Method Choice
Back1. Depth and Location: Shallow deposits favor open-pit; deep veins require underground mining.
2. Ore Grade: High-grade ores justify expensive underground operations.
3. Environmental Regulations: Strict laws may limit open-pit mining in sensitive areas.
4. Economic Viability: Solution mining is cost-effective only for specific deposits.

Vietnam 800tpd fluorite plant construction
05 Challenges in Fluorite Mining
Back1. Ore Brittleness: Fluorite crumbles easily, complicating extraction.
2. Impurities: Removing quartz or calcite adds processing steps.
3. Safety Risks: Underground mines face collapse and gas hazards.
06 Leading Fluorite Mining Regions
Back1. China: Produces ~60% of global fluorite, mostly via open-pit in Hunan and Zhejiang.
2. Mexico: Major open-pit mines in Coahuila and San Luis Potosí.
3. USA: Underground mines in Illinois and Kentucky supply acid-grade fluorite.
07 FAQs About Fluorite Mining
BackQ: Which country mines the most fluorite?
A: China produces ~60% of the world's fluorite, mostly via open-pit mining.
Q: Is fluorite mining dangerous?
A: Underground mining has risks (e.g., collapses), but modern safety protocols reduce hazards.
Q: Does fluorite mining harm the environment?
A: Open-pit mining disrupts landscapes, but reclaimed sites can restore ecosystems over time.
Q: Can fluorite be mined sustainably?
A: Yes! Recycling fluorite from industrial waste and using eco-friendly extraction tech are growing trends.
08Conclusion
BackFluorite is mined using three primary methods: open-pit (for shallow deposits), underground (for deep veins), and solution mining (experimental). The choice depends on factors like depth, ore grade, and environmental regulations. While challenges like safety risks and environmental impact exist, advances in technology and sustainable practices are making fluorite mining cleaner and more efficient.
Feel free to contact us and learn more about fluorite mining. Or maybe you can leave a message and we will reply to you soon!
 +86 18716000713
+86 18716000713 xlyin@xinhaimining.net
xlyin@xinhaimining.net




 Message
Message Chat Now
Chat Now




















