What Is the Process of Gold Tank Leaching?
 Laura
Laura
 Mar 20, 2025
Mar 20, 2025
 180
180
If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!

Zimbabwe 100TPD Gold Leaching Plant Site
Gold extraction has evolved significantly over the years, and tank leaching stands out as a highly efficient method for recovering gold from ore. Unlike traditional techniques, tank leaching uses controlled environments to maximize gold yield while minimizing environmental impact. In this guide, we’ll break down the science behind gold tank leaching, its steps, benefits, and why it’s a preferred choice in modern mining.
01 What Is Gold Tank Leaching?
BackGold tank leaching is a hydrometallurgical process where gold is dissolved from crushed ore using a chemical solution (typically cyanide) inside large, agitated tanks. This method is ideal for higher-grade ores and offers faster extraction rates compared to alternatives like heap leaching. The controlled environment ensures optimal contact between the leaching agent and gold particles, boosting efficiency.
02 Step-by-Step Process of Gold Tank Leaching
Back1. Ore Preparation
The process begins with crushing and grinding the raw ore into a fine powder. This increases the surface area, making it easier for the leaching solution to interact with gold particles. The ground ore is then mixed with water to create a slurry, which is pumped into leaching tanks.
2. Leaching in Tanks
In the tanks, a leaching agent (commonly sodium cyanide or sodium cyanide substitute-CNLITE, which is a eco-friendly gold leaching reagent) is added to the slurry. The chemical reaction dissolves gold into a liquid form. The basic reaction is:
Au + 2CN⁻ + ½O₂ + H₂O → [Au(CN)₂]⁻ + 2OH⁻
Agitators in the tanks keep the mixture moving, ensuring even distribution of the leaching agent and oxygen, which accelerates the dissolution process.
3. Separation of Gold Solution
After leaching (which can take 24–48 hours), the gold-bearing solution (called pregnant solution) is separated from the leftover solids. This is done using filtration or thickening systems. The solids, now depleted of gold, become tailings.
4. Gold Recovery
The pregnant solution undergoes further processing to extract gold:
1. Carbon Adsorption: Activated carbon is used to adsorb gold from the solution (similar to CIP/CIL methods).
2. Electrowinning: An electric current passes through the solution, causing gold to plate onto steel wool electrodes.
3. Precipitation: Zinc or other chemicals are added to precipitate gold from the solution.
The recovered gold is then smelted into bars for purification.
5. Tailings Management
Tailings are treated to neutralize residual cyanide (e.g., using hydrogen peroxide) and stored in secure facilities to prevent environmental contamination. Modern systems often recycle water and chemicals to reduce waste.
03 Advantages of Tank Leaching
Back1. High Recovery Rates: Up to 95% gold extraction efficiency.
2. Speed: Faster than heap leaching due to agitation and controlled conditions.
3. Flexibility: Works well with high-grade or complex ores.
4. Environmental Control: Reduced risk of leaks compared to open-air methods.
04 Challenges and Considerations
Back1. Cost: Requires significant investment in tanks, agitators, and grinding equipment.
2. Energy Use: Agitation and pumping consume more energy.
3. Cyanide Management: Strict protocols are needed to handle toxic chemicals safely.
05 Tank Leaching vs. Heap Leaching: Key Differences
Back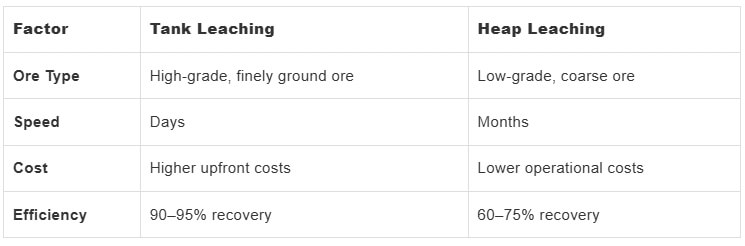
Tank Leaching vs. Heap Leaching
06 Environmental and Safety Practices
Back1. Cyanide Alternatives: Some mines use thiosulfate or chloride solutions for eco-friendlier leaching.
2. Closed-Loop Systems: Prevent chemical leakage by recycling water and solutions.
3. Regulatory Compliance: Mines must adhere to strict guidelines for tailings storage and chemical use.
07Conclusion
BackGold tank leaching is a cornerstone of modern gold extraction, balancing efficiency, speed, and environmental responsibility. By dissolving gold in controlled tank environments, miners achieve higher yields while mitigating risks associated with traditional methods. As technology advances, innovations like non-cyanide reagents and automation promise to make this process even more sustainable.
Feel free to contact us and learn more about gold tank leaching process! Or maybe you can leave a message and we will reply to you soon.
 +86 18716000713
+86 18716000713 xlyin@xinhaimining.net
xlyin@xinhaimining.net




 Message
Message Chat Now
Chat Now