Nickel Processing Flow: Comprehensive Guide
 Sheena
Sheena
 Dec 26, 2024
Dec 26, 2024
 851
851
If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!
Flotation-and-concentrate-dewatering-system
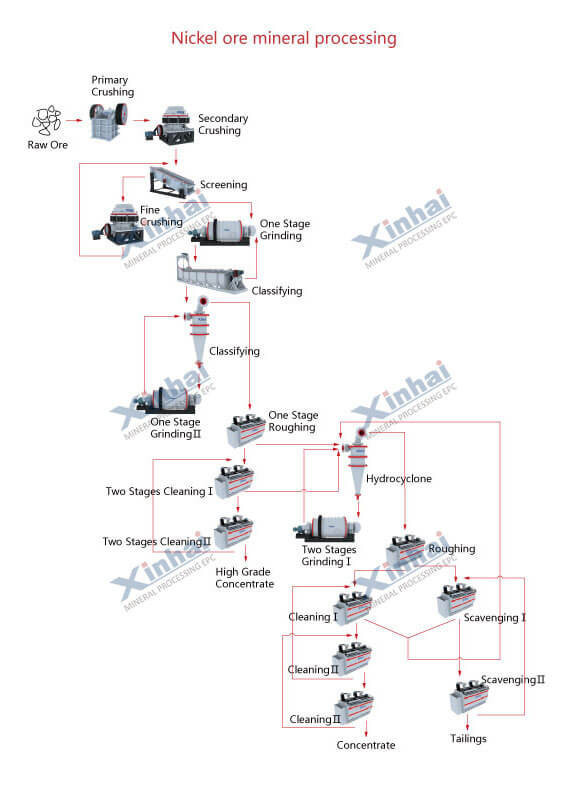
Nickel is a vital industrial metal, widely used in the production of stainless steel, batteries, and various alloys. Understanding the nickel processing flow chart is essential for industries to optimize extraction and refining methods. This article delves into the steps involved in nickel ore processing and highlights the critical equipment required in each stage.
01Overview of Nickel Ore
BackNickel ore primarily occurs in two forms: laterite and sulfide deposits.
Laterite ores: Found near the earth's surface, typically in tropical climates. They are rich in iron and nickel oxides.
Sulfide ores: Found deeper underground, containing nickel in the form of sulfide minerals such as pentlandite.
The processing methods differ based on the type of ore, but both follow a series of common steps.
02Mining and Extraction
Back
1. Process:
The initial stage involves mining nickel ore from deposits. Open-pit and underground mining methods are used depending on the location and depth of the ore body. After extraction, the ore is transported to the processing plant.
03Crushing and Screening
Back1. Process:
The mined ore is reduced in size using crushers to ensure efficient processing. Screening separates materials by size, removing unwanted debris or oversized rocks.
2. Key Equipment:
Jaw Crushers: For initial crushing.
Cone Crushers: For secondary and fine crushing.
Vibrating Screens: To classify crushed materials into specific size ranges.
04Grinding and Milling
Back1. Process:
The crushed ore is further reduced to a fine powder to release nickel minerals from the gangue. Grinding ensures the ore particles are of uniform size, which is crucial for downstream processes.
2. Key Equipment:
Ball Mills: For wet or dry grinding of ore.
Rod Mills: For more precise grinding needs.
Hydrocyclones: To classify and recycle oversized particles for further grinding.
05Beneficiation
Back1. Process:
Beneficiation separates valuable nickel minerals from the gangue using physical or chemical methods. Techniques vary based on ore type:
For sulfide ores: Froth flotation is the most common technique.
For laterite ores: Hydrometallurgical methods like leaching are employed.
2. Key Equipment:
Flotation Cells: To separate nickel sulfide minerals using reagents and air bubbles.
Leach Tanks: For dissolving nickel oxides in laterite ores.
Thickeners: To concentrate the slurry by removing excess water.
06Waste Management and Environmental Considerations
Back1. Process:
Nickel processing generates tailings, slags, and emissions. Proper waste management ensures environmental sustainability.
2. Key Equipment:
Tailings Dams: To store waste materials safely.
Dust Collectors: To minimize airborne particles.
Water Treatment Plants: To recycle and purify water used in processing.
07Conclusion
BackNickel processing involves multiple stages, each requiring specialized equipment to achieve efficiency and sustainability. Understanding the flow chart from mining to refining is crucial for industries aiming to maximize yield while minimizing environmental impact. By leveraging advanced technologies and adhering to stringent environmental standards, nickel producers can ensure sustainable operations and meet growing global demand.
 +86 18716000713
+86 18716000713 xlyin@xinhaimining.net
xlyin@xinhaimining.net




 Message
Message Chat Now
Chat Now